- Patients Patients
Reproductive Genetics Testing
Patient Resources
Cost & Billing
- Providers Providers
- Genetic Counseling
- Login Login
- Estimate My Cost

Women's Health Testing
Diabetes Risk Testing
There are an estimated 84 million adults 18 years and older in the U.S. who are pre-diabetic or at risk for developing diabetes and another 7 million with undiagnosed diabetes.1

Recommendations by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists2 state testing for type 2 diabetes risk in asymptomatic people should be considered:
- Adults of any age who are overweight or obese and who have one or more additional risk factors for diabetes (BMI > 25 kg/m2 or >23 kg/m2 in Asian Americans); and
- One or more additional risk factors
- Physical inactivity
- First degree relative with diabetes
- High-risk race/ethnicity (eg, African American, Latino, Native American, Asian American, Pacific Islander)
- Women who delivered a baby weighing 9 lbs or more or were diagnosed with GDM and normal postpartum screening test results, repeat testing 1 to 3 years
- Hypertension (>140/90 mmHG or on therapy for hypertension)
- HDL cholesterol level <35 mg/dl and/or a triglyceride level of >250 mg/dl
- Women with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Hemoglobin A1C >5.7%, IGT or IFG on previous testing
- Other clinical conditions associated with insulin resistance (eg, severe obesity, acanthosis nigricans)
- History of CVD
Informational Brochures
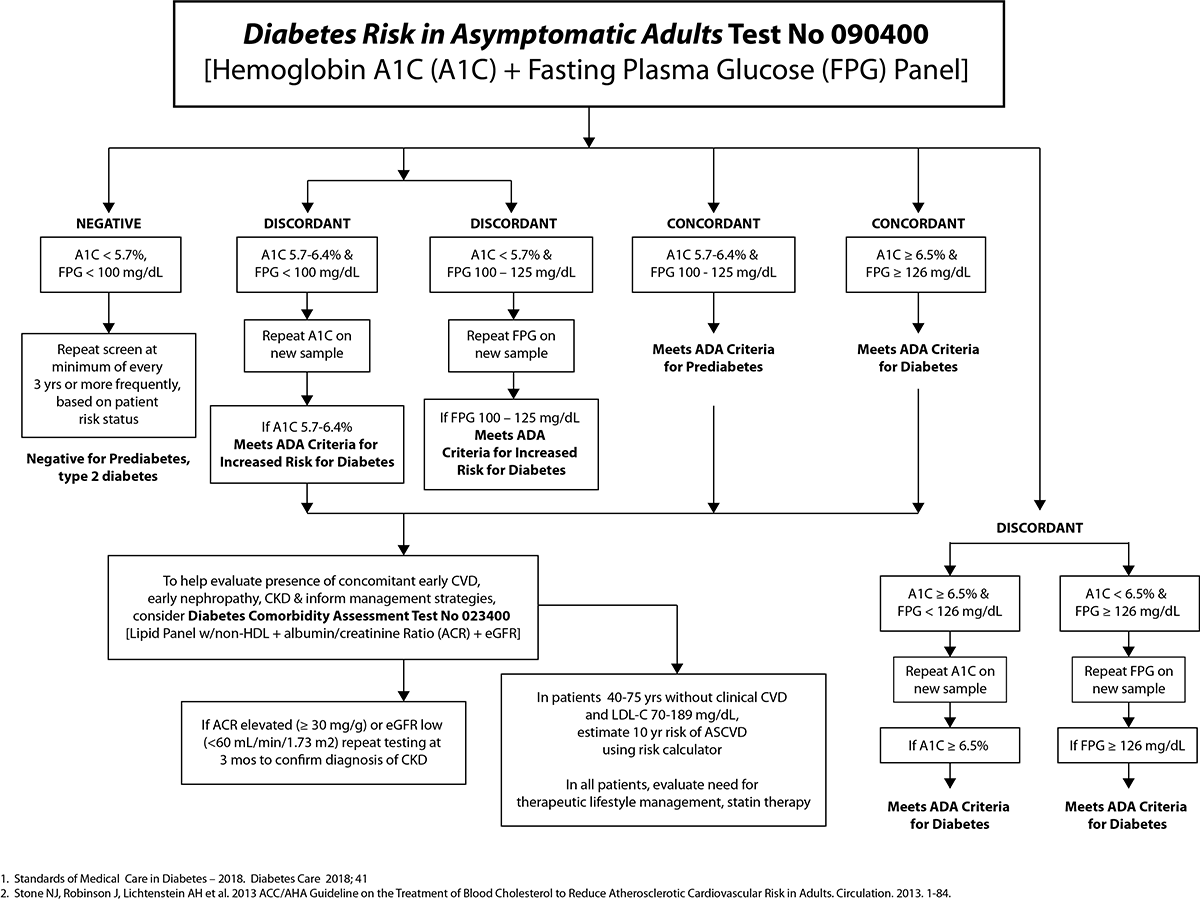
Suggested Approach to Testing
A Suggested Approach to Testing Based on ACC/AHA 2013 Guidelines, 2018 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes and general practice standards.3,4
Reference
- National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2017. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Center for Disease Control. Pages 1-20
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Well Women Recommendations. High-Risk Factors. Available at: https://www.acog.org/About-ACOG/ACOG-Departments/Annual-Womens-Health-Ca...
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes Care – 2018. American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2018;S1:S1-S159
- Stone NJ, Robinson J, Lichtenstein AH, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;114:S1-S45


